Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Definition
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory illness that causes fever, coughing, and shortness of breath, but many other symptoms can occur. COVID-19 is caused by a highly infectious virus. Most people get mild to moderate illness. Older adults and people with certain health conditions are at high risk for severe illness and death. More than one million people in the United States have died from COVID-19.
Alternative Names
Coronavirus - 2019; Coronavirus - novel 2019; 2019 Novel coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2
Causes
COVID-19 is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2). Coronaviruses are a family of viruses that can affect people and animals. They can cause mild to moderate respiratory illnesses, such as the common cold. Some coronaviruses can cause severe illness that can lead to pneumonia and even death.
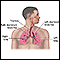
COVID-19 most readily spreads to people within close contact (about 6 feet or 2 meters). When someone with the illness coughs, sneezes, sings, talks, or breathes, droplets and very small particles spray into the air. You can catch the illness if you breathe in these droplets or particles or they land on your eyes, nose, or mouth.
In some instances, COVID-19 may spread through the air and infect people who are more than 6 feet away. Small droplets and particles can remain in the air for minutes to hours. This is called airborne (or aerosol) transmission, and it occurs especially in enclosed spaces with poor ventilation. However, it is more common for COVID-19 to spread through close contact.
Less often, the illness can spread if you touch a surface with the virus on it, and then touch your eyes, nose, mouth, or face. But this is thought to be a much less common way in which the virus spreads.
COVID-19 can spread from person to person quickly. As the virus spreads, it can change, and new variants of the virus will occur. Different variants may spread more quickly or be more resistant to treatments or vaccines. Taking steps to slow the spread of the virus, such as by getting a COVID-19 vaccine, can help slow the development of new variants.
While the United States Federal COVID-19 Public Health Emergency has ended, COVID-19 is still a health concern, especially for people at high risk of serious illness.
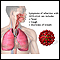
Symptoms
COVID-19 symptoms range from mild to severe. Older people and people with certain existing health conditions have a higher risk of developing severe illness and death. Health conditions that increase this risk include:
- Asthma (if it's moderate or severe)
- Cancer
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
- Cystic fibrosis
- Dementia
- Diabetes (type 1 and type 2)
- Down syndrome or other disabilities
- Heart disease and stroke
- HIV
- Kidney, lung, or liver disease
- Mental health conditions
- Overweight and obesity (BMI of 25 kg per square meter or above)
- Physical inactivity
- Pregnancy
- Organ or stem cell transplantation
- Sickle cell disease or thalassemia
- Smoking (current or former)
- Substance use disorders
- Tuberculosis
- Weak immune system (immunocompromised)
Symptoms of COVID-19 may include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Cough
- Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
- Headache
- Loss of sense of taste or smell
- Sore throat
- Stuffy or runny nose
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
This is not a complete list of possible symptoms. Symptoms may change with new variants of the virus.
Some people may have no symptoms at all. Many people have some, but not all of these symptoms. Symptoms can also vary, depending on whether you are vaccinated and boosted.
Symptoms may appear within 2 to 14 days after being exposed. Most often, symptoms appear around 5 days after exposure. However, you can spread the virus even when you do not have symptoms.
More severe symptoms that require seeking medical help right away include:
- Trouble breathing
- Chest pain or pressure that persists
- Confusion or inability to wake up
- Blue lips or face (cyanosis)
- Any other symptoms that are severe or that concern you
Exams and Tests
If you have symptoms of COVID-19, you can perform a self-test. Your health care provider also may decide to test you for the disease.
If you get tested for COVID-19, swabs from the back of the nose, the front of the nose, or the throat will be collected to test for SARS-CoV-2.
Treatment
If you are recovering at home, supportive care is given to help relieve symptoms. People with severe illness will be treated in the hospital.
The types of medicines given may vary depending upon how sick you are, your risk factors for serious illness from the disease, your age, and possibly what variant of the virus is causing the infection.
If you test positive for COVID-19, your provider may recommend antiviral medicines.
If given soon after you become infected (5 to 7 days, depending on the medicine), these medicines help your immune system fight off the virus. They may be given to adults and children with mild to moderate illness who are not hospitalized. These medicines include:
- Nirmatrelvir with ritonavir (Paxlovid), an antiviral medicine, to help slow the virus. It is a pill you take at home.
- Remdesivir (Veklury), an antiviral medicine, to help slow the virus. This medicine is given through the vein (IV). You will need to go to a health care facility for 3 days in a row to receive this medicine.
- Molnupiravir (Lagevrio), an antiviral medicine used only for adults. It is a pill you take at home.
If you are being cared for in the hospital and are receiving oxygen therapy, treatment for COVID-19 may include the following medicines:
- Remdesivir, an antiviral medicine, to help slow the virus.
- Dexamethasone, a steroid medicine, to help reduce an overactive immune response in the body. If dexamethasone is not available, you may be given another corticosteroid such as prednisone, methylprednisolone, or hydrocortisone.
- You may be given one or the other medicine or both medicines together.
- Baricitinib or tocilizumab to help reduce immune system activity, depending on your condition.
- Medicines for any complications from the disease. For example, you may be given blood thinners to help reduce the chance of blood clots, or you may have dialysis if your kidneys do not function properly.
Based on available evidence, current treatment guidelines from the National Institutes of Health recommend against using some medicines for COVID-19, including chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and ivermectin. Do not take any medicines to treat COVID-19 except those prescribed by your provider. Check with your provider before treating yourself or a loved one with vitamins, nutrients, or any medicines prescribed in the past for other health problems. Since some COVID-19 medicines have interactions with other medicines or supplements you may be taking, always check with your provider before starting them.
Possible Complications
Complications can include:
- Long COVID, which is defined by lasting COVID-19 symptoms that continue 4 weeks or longer after infection with the virus (post-acute sequelae of SARS CoV-2 infection [PASC])
- Damage to the heart and blood vessels, kidneys, brain, skin, eyes, and gastrointestinal organs
- Respiratory failure
- Death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
You should contact your provider:
- If you have symptoms and think you may have COVID-19
- If you have COVID-19 and you are in a group for whom antiviral medicine may be given
- If you have COVID-19 and your symptoms are getting worse
Call 911 or the local emergency number if you have:
- Trouble breathing
- Chest pain or pressure
- Confusion or inability to wake up
- Blue lips or face
- Any other symptoms that are severe or concern you
Prevention
You can take steps to protect yourself and others from COVID-19:
- Get a COVID-19 vaccine.
- If you have children, make sure they get a COVID-19 vaccine.
- If you have COVID-19 or have symptoms of it stay at home and avoid contact with other people.
- Wear a well-fitted face mask or respirator.
- Practice good hygiene. Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Wash your hands many times a day with soap and running water for at least 20 seconds. Use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer (at least 60% alcohol) if soap and water are not available.
- Take steps for cleaner air in your home. Open windows, use fans and portable high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) cleaners, and set the fan on your furnace or air conditioning to on.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. COVID-19: types of COVID-19 treatment. www.cdc.gov/covid/treatment/. Updated May 8, 2025. Accessed June 5, 2025.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. COVID-19: long COVID basics. www.cdc.gov/long-covid/about/index.html. Updated July 24, 2025. Accessed December 1, 2025.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Respiratory illnesses: preventing respiratory illnesses. www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/prevention/index.html. Updated August 18, 2025. Accessed December 1, 2025.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccines. www.cdc.gov/covid/vaccines/stay-up-to-date.html. Updated November 19, 2025. Accessed December 1, 2025.
Del Rio C, Gandhi M, Cohen MS. COVID-19: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and community prevention. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 336.