Telangiectasia
Definition
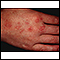
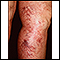
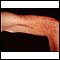
Telangiectasias are small, widened blood vessels on the skin. They are usually harmless, but may be associated with several diseases.
Alternative Names
Vascular ectasias; Spider angioma
Causes
Telangiectasias may develop anywhere in the body. But they are most easily seen on the skin, mucous membranes, and whites of the eyes. Usually, they do not cause symptoms. Some telangiectasias bleed and cause significant problems. Telangiectasias may also occur in the brain or intestines and cause major problems from bleeding.
Causes of telangiectasias in the skin include:
- Aging
- Problem with genes
- Pregnancy
- Sun exposure
- Varicose veins
- Overuse of steroid creams
- Trauma to the area
Diseases associated with telangiectasias include:
- Ataxia-telangiectasia (disease that affects the skin, balance, coordination, and other areas of the body)
- Bloom syndrome (inherited disease that causes short stature, skin sensitivity to ultraviolet rays of the sun, and redness of the face)
- Cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita (skin disease causing patches of redness)
- Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome)
- Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome (disease that causes port-wine stain, varicose veins, and soft tissue problems)
- Nevus flammeus (port-wine stain)
- Rosacea (skin condition that causes redness of the face)
- Sturge-Weber disease (disease that involves port-wine stain and nervous system problems)
- Xeroderma pigmentosum (disease in which the skin as well as the tissue covering the eye are extremely sensitive to ultraviolet light)
- Lupus (immune system disease)
- CREST syndrome (a type of scleroderma that involves the buildup of scar-like tissue in the skin and elsewhere in the body and damages the cells that line the walls of small arteries)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you notice enlarged vessels in the skin, mucous membranes, or eyes.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms, including:
- Where are the blood vessels located?
- Do they bleed easily and without reason?
- What other symptoms are present?
Tests may be needed to diagnose or check for a medical condition. Tests may include:
Sclerotherapy is the treatment for telangiectasias on the legs. In this procedure, a saline (salt) solution or other chemical is injected directly into the spider veins on the legs. Laser treatment is typically used to treat telangiectasias of the face.
References
Kelly R, Baker C. Other vascular disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 106.
Patterson JW. Vascular tumors. In: Patterson JW, ed. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2025:chap 39.