Abdominal exploration
Definition
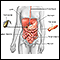
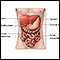
Abdominal exploration is surgery to look at the organs and structures in your belly area (abdomen). This includes your:
- Appendix
- Bladder
- Gallbladder
- Intestines
- Kidney and ureters
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Spleen
- Stomach
- Uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries (in women)
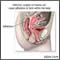
Surgery that opens the abdomen is called a laparotomy.
Alternative Names
Exploratory surgery; Laparotomy; Exploratory laparotomy
Description
Exploratory laparotomy is done while you are under general anesthesia. This means you are asleep and feel no pain.
Your surgeon makes a cut into the abdomen and examines the abdominal organs. The size and location of the surgical cut depend on the specific health concern.
A biopsy can be taken during the procedure.
Laparoscopy describes a procedure that is performed with a tiny camera placed inside the abdomen. If possible, laparoscopy will be done instead of laparotomy.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Your health care provider may recommend a laparotomy if imaging tests of the abdomen, such as x-rays and CT scans, have not provided an accurate diagnosis.
Exploratory laparotomy may be used to help diagnose and treat many health conditions, including:
- Cancer of the ovary, colon, pancreas, liver
- Endometriosis
- Gallstones
- Hole in the intestine (intestinal perforation)
- Acute appendicitis
- Diverticulitis
- Acute or chronic pancreatitis
- Liver abscess
- Pockets of infection (retroperitoneal abscess, abdominal abscess, pelvic abscess)
- Pregnancy outside of the uterus (ectopic pregnancy)
- Scar tissue in the abdomen (adhesions)
Risks
Risks of anesthesia and surgery in general include:
- Reactions to medicines
- Breathing problems
- Bleeding, blood clots, infection
Risks of this surgery include:
- Incisional hernia
- Damage to organs in the abdomen
Before the Procedure
You will visit with your provider and have medical tests before your surgery. Your provider will:
- Do a complete physical exam.
- Make sure other medical conditions you may have, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, are under control.
- Perform tests to make sure that you will be able to tolerate the surgery.
- If you are a smoker, you should stop smoking several weeks before your surgery. Ask your provider for help.
Tell your surgeon or nurse if:
- You are or could be pregnant
- You are taking any medicines, including drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription
During the week before your surgery:
- You may be asked to temporarily stop taking medicines that keep your blood from clotting. These medicines are called blood thinners. This includes over-the-counter medicines and supplements such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), and vitamin E. Many prescription medicines are also blood thinners.
- Ask your surgeon which medicines you should still take on the day of surgery.
On the day of surgery:
- Follow instructions about when to stop eating and drinking.
- Take the medicines your surgeon told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Arrive at the hospital on time.
Outlook (Prognosis)
You should be able to start eating and drinking normally about 2 to 3 days after the surgery. How long you stay in the hospital depends on the severity of the problem. Complete recovery usually takes about 4 to 6 weeks.
References
Landmann A, Bonds M, Postier R. Acute abdomen. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 46.
Young S, Tsai S. Management of periampullary cancer. In: Cameron JL, Cameron AM, eds. Current Surgical Therapy. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:589-599.