Incontinentia pigmenti
Definition
Incontinentia pigmenti (IP) is a rare skin condition passed down through families. It affects the skin, hair, eyes, teeth, and nervous system.
Alternative Names
Bloch-Sulzberger syndrome; Bloch-Siemens syndrome
Causes
IP is caused by an X-linked dominant genetic variant that occurs on a gene known as IKBKG.
Because the variant gene occurs on the X chromosome, the condition is most often seen in females. When it occurs in males, it is usually lethal in the fetus and results in miscarriage.
Symptoms
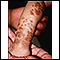
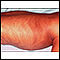
With the skin symptoms, there are 4 stages. Infants with IP are born with streaky, blistering areas. In stage 2, when the areas heal, they turn into rough bumps. In stage 3, the bumps go away, but leave behind darkened skin, called hyperpigmentation. After several years, the skin returns to normal. In stage 4, there may be areas of lighter-colored skin (hypopigmentation) that are thinner.
IP is associated with central nervous system problems, including:
- Delayed development
- Loss of movement (paralysis)
- Intellectual disability
- Muscle spasms
- Seizures
People with IP may also have abnormal teeth, hair loss, and vision problems.
Exams and Tests
Your child's health care provider will perform a physical exam, look at the eyes, and test muscle movement.
There may be unusual patterns and blisters on the skin, as well as bone abnormalities. An eye exam may reveal cataracts, strabismus (crossed eyes), or other problems.
To confirm the diagnosis, these tests may be done:
- Blood tests
- Skin biopsy
- CT or MRI scan of the brain
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for IP. Treatment is aimed at the individual symptoms. For example, glasses may be needed to improve vision. Medicine may be prescribed to help control seizures or muscle spasms.
Support Groups
More information and support groups for people with IP and their families can be found at:
- National Foundation for Ectodermal Dysplasias -- www.nfed.org/about-us/how-we-help/
- National Organization for Rare Disorders -- rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/incontinentia-pigmenti/
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well a person does depends on the severity of central nervous system involvement and eye problems.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have a family history of IP and are considering having children
- Your child has symptoms of this disorder
Prevention
Genetic counseling may be helpful for those with a family history of IP who are considering having children.
References
Islam MP, Roach ES. Neurocutaneous syndromes. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 99.
James WD. Genodermatoses and congenital anomalies. In: James WD, ed. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2026:chap 22.
Patterson JW. Disorders of pigmentation. In: Patterson JW, ed. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2025:chap 11.