Herpangina
Definition
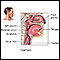
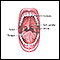
Herpangina is a viral illness that involves ulcers and sores (lesions) inside the mouth, a sore throat, and fever.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a related topic.
Causes
Herpangina is a common childhood infection. It is most often seen in children ages 3 to 10, but it can occur in any age group.
It is most often caused by Coxsackie group A viruses. These viruses are contagious. Your child is at risk for herpangina if someone at school or home has the illness.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Sore throat, or painful swallowing
- Ulcers in the mouth and throat, and similar sores on the feet, hands, and buttocks
The ulcers most often have a white to whitish-gray base and a red border. They may be very painful. In most cases, there are only a few sores.
Exams and Tests
Tests are not normally necessary. Your health care provider can most often diagnose this condition by doing a physical exam and asking questions about the child's symptoms and medical history.
Treatment
The symptoms are treated as necessary:
- Take acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Motrin) by mouth for fever and discomfort as the provider recommends.
- Increase fluid intake, especially cold milk products. Gargle with cool water or try eating fruit-flavored ice pops. Avoid hot beverages and citrus fruits.
- Eat a non-irritating diet. (Cold milk products, including ice cream, are often the best choices during herpangina infection. Fruit juices are too acidic and tend to irritate the mouth sores.) Avoid spicy, fried, or hot foods.
- Use topical anesthetics for the mouth (these may contain benzocaine or xylocaine and are usually not required).
Outlook (Prognosis)
The illness normally clears up within a week.
Possible Complications
Dehydration is the most common complication, but it can be treated by your provider.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- Fever, sore throat, or mouth sores last for more than 5 days
- Your child is having trouble drinking liquids or looks dehydrated
- Fever becomes very high or does not go away
Prevention
Good handwashing can help prevent the spread of the viruses that lead to this infection.
References
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Viral diseases. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 19.
Messacar K, Abzug MJ. Nonpolio enteroviruses. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 277.
Romero JR. Coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, and numbered enteroviruses (EV-A71, EVD-68, EVD-70). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 172.